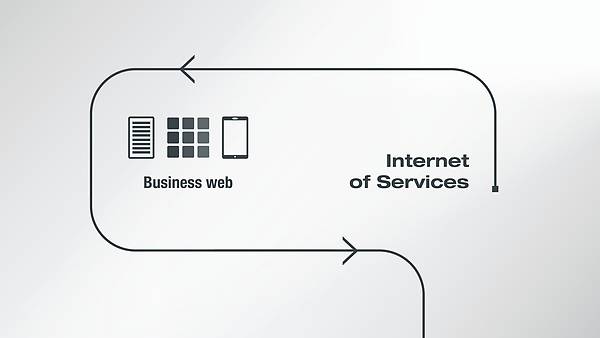
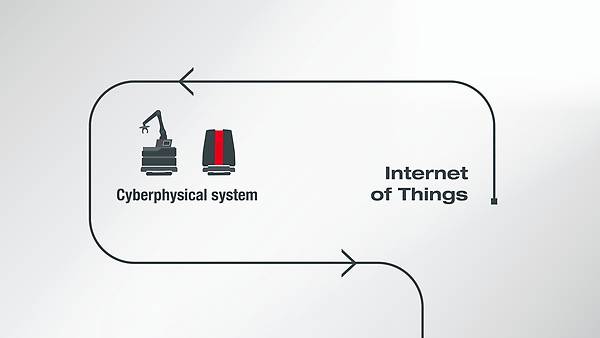
Big Data, embedded computing , mobile internet and cloud computing are new digital technologies that will have an impact on future production environments. The fourth industrial revolution has begun.
Industry 3.0 describes the age of computer-aided automation that generated major productivity gains from the 1970s onwards. Industry 2.0 marks the start of mass production using electrical energy, while Industry 1.0 describes the transition from muscle power to physically generated energy in the form of steam and water.
But what exactly is Industry 4.0?
This term covers all the new opportunities for digitally networked production, such as assembly, maintenance, repair, marketing and disposal. This includes machinery and components that are no longer just networked and centrally controlled (Industry 3.0) but also make independent decisions decentrally based on digital information and incorporate them into the overall production system. Adaptive systems will be created over time.
Industry 4.0. Terms and definitions
In discussions relating to Industry 4.0 or digitalization, a number of terms are frequently used. Here are three that are important for us in these contexts: